On-Grid vs Off-Grid Solar System Comparison 2026: Cost, Benefits & Which Is Better
Introduction: Why India Is Actively Choosing Solar Power?
India is standing at a decisive moment in its energy journey. Rising electricity tariffs, frequent power cuts in several regions, and growing awareness about climate change are pushing households and businesses to explore solar energy. Rooftop solar installations are no longer a luxury — they are quickly becoming a necessity.
Yet, one major question stops most people from moving forward:
Should I choose an on-grid or an off-grid solar system?
This detailed On-grid vs off-grid solar system comparison will help you make a confident, informed decision. We will break down how each system works, compare costs, maintenance, reliability, subsidies, real-life use cases, and long-term returns — all in simple, human-friendly language.
There is no one-size-fits-all answer. The right solar system depends on where you live, how reliable your electricity supply is, your budget, and how much energy independence you want.
Table of Contents:
Understanding Solar Power Systems in Simple Terms
Before comparing, let’s clarify what solar systems actually do.
A solar power system converts sunlight into electricity using photovoltaic (PV) panels. This electricity can be:
- Used immediately
- Stored in batteries
- Sent to the electricity grid
- Or managed through a mix of all three
The difference between on-grid and off-grid solar systems lies mainly in grid connection and energy storage.
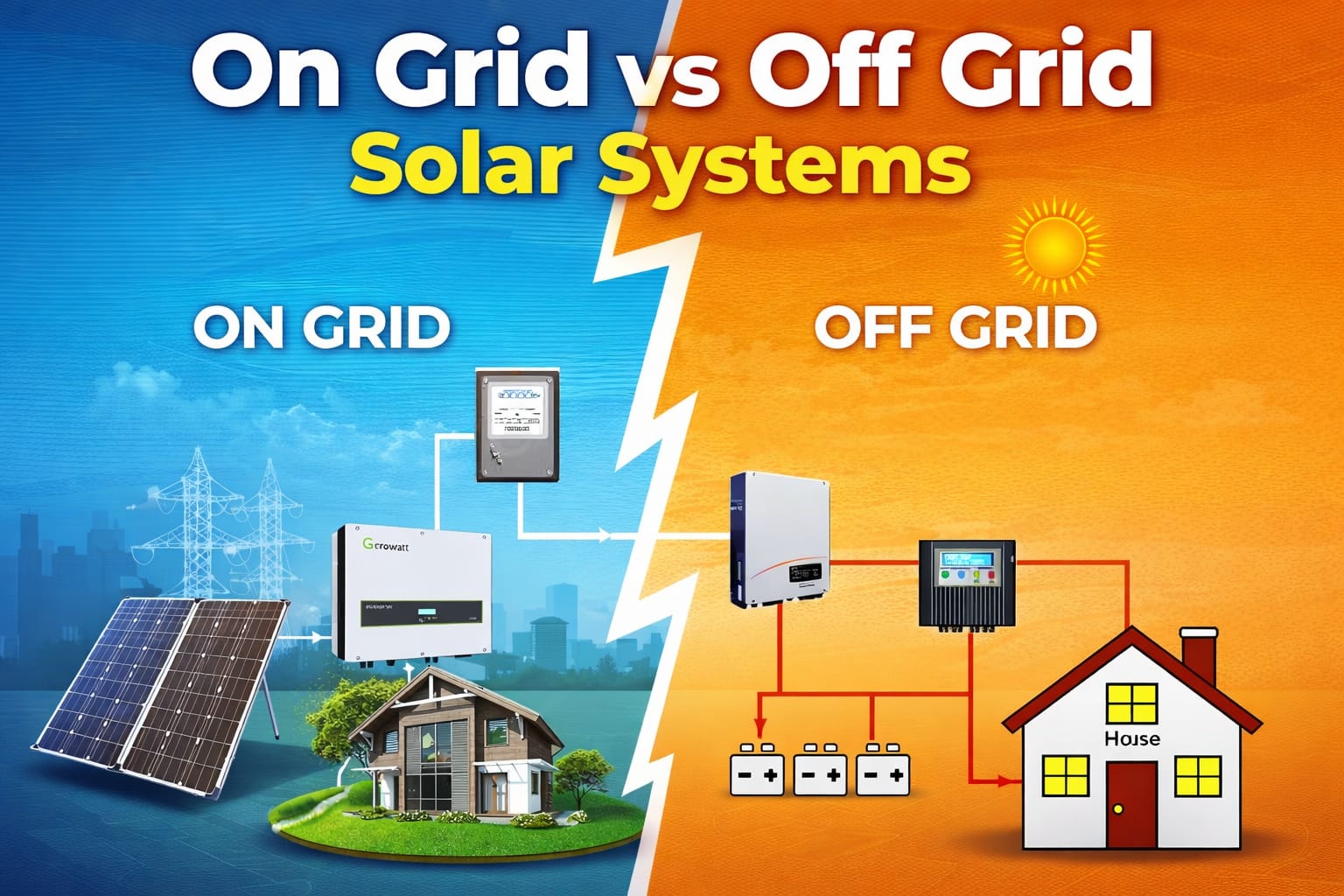
What Is an On-Grid Solar System?
Definition Explained Simply –
An on-grid solar system (also called grid-tied solar) is connected directly to your local electricity grid. It produces electricity during the day and works alongside the grid to meet your power needs.
There are no batteries involved.

When your solar panels produce more electricity than you use, the excess power is exported to the grid. When solar production is low (night or cloudy weather), electricity is imported from the grid.
How an On-Grid Solar System Works?
- Solar panels generate DC electricity from sunlight
- Solar inverter converts DC to AC power
- Your home uses solar power first
- Extra electricity goes to the grid
- Net meter records units sent and received
This flow makes on-grid systems extremely efficient and cost-effective for areas with reliable electricity supply.
Net Metering: The Key Advantage
Net metering is the backbone of on-grid solar economics.
With net metering:
- Exported solar units earn credits
- Imported grid units consume credits
- You pay only for the “net” electricity used
In many Indian states, this results in 70–95% reduction in electricity bills.
Ideal Use Case for On-Grid Solar –
On-grid systems are best suited for:
- Urban homes
- Apartments (with rooftop access)
- Offices and commercial buildings
- Cities with stable power supply
Example:
A 5kW on-grid solar system in Pune can reduce a ₹6,000 monthly bill to under ₹500 after net metering.
What Is an Off-Grid Solar System?
Complete Energy Independence Explained –
An off-grid solar system works independently of the electricity grid. It generates, stores, and supplies electricity entirely on its own.
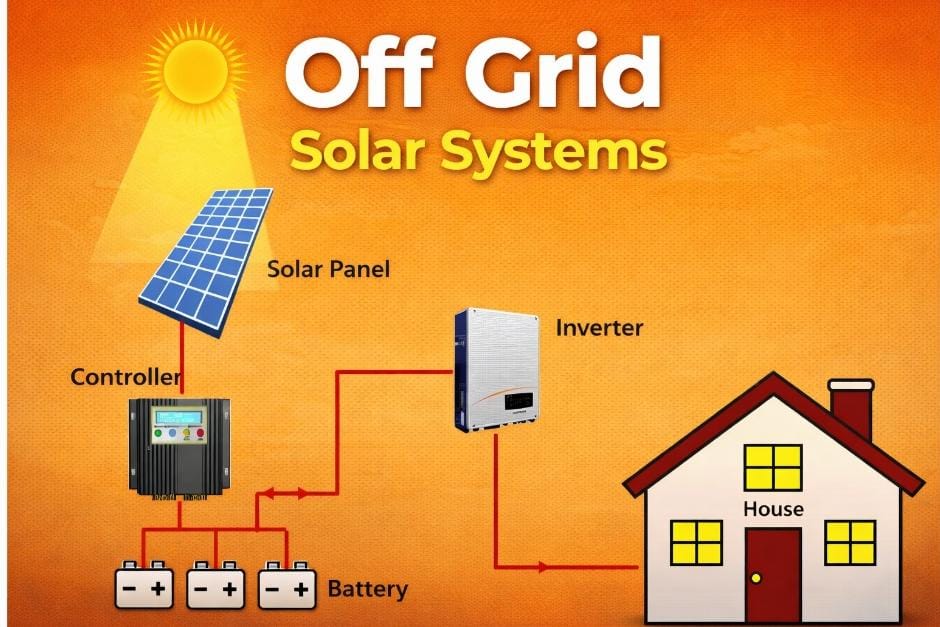
These systems include battery storage, making them suitable for locations where:
- Grid power is unavailable
- Power cuts last several hours
- Diesel generators are expensive
How an Off-Grid Solar System Works?
- Solar panels generate DC electricity
- Charge controller regulates battery charging
- Batteries store excess energy
- Inverter converts stored DC into AC power
- Electricity is supplied day and night
Even during complete blackouts, off-grid systems continue to operate normally.
Battery Types Used in Off-Grid Systems –
| Battery Type | Average Life | Maintenance | Cost Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flooded Lead-Acid | 3–5 years | High | Low |
| AGM / Gel | 4–7 years | Medium | Medium |
| Lithium-Ion (LiFePO4) | 8–15 years | Very Low | High |
| Saltwater | 10+ years | None | High |
Batteries significantly increase the cost but provide full independence.
Ideal Use Case for Off-Grid Solar –
Off-grid solar systems are best for:
- Remote villages
- Hill stations
- Farms and agricultural pumps
- Islands and border areas
- Clinics, schools, eco-resorts
Example:
A rural healthcare center in Odisha running on off-grid solar avoids diesel costs and gets uninterrupted power for lifesaving equipment.
On-Grid vs Off-Grid Solar System Comparison Table:
| Feature | On-Grid Solar System | Off-Grid Solar System |
|---|---|---|
| Grid Connection | Required | Not required |
| Battery Storage | No | Yes |
| Power During Blackouts | No | Yes |
| Initial Cost | Low | High |
| Government Subsidy | High | Limited |
| Maintenance | Minimal | High |
| Electricity Bill Savings | Very High | Moderate |
| Energy Independence | Partial | Complete |
| Best For | Cities & towns | Remote locations |
This On-grid vs off-grid solar system comparison shows that cost and reliability are the biggest deciding factors.
On-grid vs off-grid solar system comparison (Cost) in India (2026 Estimates):
Initial Investment –
| System Size | On-Grid Cost | Off-Grid Cost |
|---|---|---|
| 3kW | ₹1.2–1.8 lakh | ₹2.5–3.5 lakh |
| 5kW | ₹2.2–2.8 lakh | ₹4.5–6 lakh |
| 10kW | ₹4–5 lakh | ₹9–12 lakh |
5-Year Ownership Cost Comparison –
| Expense | On-Grid | Off-Grid |
|---|---|---|
| Installation | Low | High |
| Maintenance | Very Low | Moderate |
| Battery Replacement | None | High |
| Total 5-Year Cost | Low | Very High |
Government Subsidies & Schemes:
On-Grid Solar Subsidy (PM Surya Ghar Yojana) –
- ₹18,000 per kW up to 3kW
- Additional subsidy for group housing societies
- Direct transfer to consumer bank account
Off-Grid Subsidy –
- Available mainly for:
- Tribal areas
- Islands
- Border regions
- Agricultural solar pumps (PM-KUSUM)
Hybrid Solar Systems: A Balanced Alternative:
A hybrid system combines:
- Grid connection
- Battery backup
- Solar generation
Who Should Choose Hybrid?
- Semi-urban homes
- Areas with daily power cuts
- Homes running work-from-home setups
Hybrid systems cost more than on-grid but offer peace of mind during outages.
On-grid vs off-grid solar system comparison of Return on Investment (ROI):
| System Type | Average ROI Period |
|---|---|
| On-Grid | 3.5–5 years |
| Hybrid | 5–8 years |
| Off-Grid | 8–12 years |
On-grid systems deliver the fastest financial returns in India.
On-grid vs off-grid solar system comparison of Maintenance Requirements:
On-Grid Maintenance –
- Panel cleaning: once a month
- Inverter check: once a year
- Cost: ₹2,000–3,000 annually
Off-Grid Maintenance –
- Battery monitoring
- Periodic replacements
- Higher servicing costs
On-grid vs off-grid solar system comparison of Environmental Impact:
| Factor | On-Grid | Off-Grid |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon Reduction | Very High | High |
| Battery Waste | None | Significant |
| Lifecycle Emissions | Lower | Higher |
From an environmental standpoint, on-grid solar is cleaner due to no battery dependency.
Solar Panel Price in India 2026: Complete Cost Guide (1kW, 3kW, 5kW, 10kW + With Subsidy)
Frequently Asked Questions (Q&A):
Q1. Which system is better for Indian cities?
On-grid solar systems due to stable electricity supply and subsidies.
Q2. Can on-grid solar work during power cuts?
No. Safety regulations automatically shut it down.
Q3. Is off-grid solar worth the cost?
Yes, only if grid power is unreliable or unavailable.
Q4. Can I upgrade later?
On-grid → Hybrid is easy
Off-grid expansion is complex and costly
Q5. Which system lasts longer?
Panels last 25+ years in both systems, but batteries reduce off-grid lifespan economics.
Final Verdict: Which Solar System Should You Choose?
This On-grid vs off-grid solar system comparison clearly shows:
- Choose On-Grid if you live in a city or town with reliable electricity
- Choose Off-Grid only if power cuts exceed 8 hours daily or there is no grid access
- Choose Hybrid if you want savings + backup
Solar is no longer just an environmental choice — it’s a smart financial investment. The key is matching the system to your real-world needs, not assumptions.
Key Takeaway
The sun gives free energy every day.
The right solar system decides how effectively you use it.
If planned correctly, solar power can reduce your electricity bills, protect you from tariff hikes, and contribute to a cleaner future — for the next 25 years and beyond.




