
Off-Grid Solar Systems in India: Cost, Benefits, Installation Process & Complete Guide
India’s energy landscape is undergoing a silent but powerful transformation. As electricity demand rises, power cuts persist in rural and semi-urban areas, and energy costs continue to fluctuate, off-grid solar systems in India are emerging as a practical, affordable, and future-ready solution. Once considered an alternative only for remote villages, off-grid solar power is now being adopted by homes, farms, schools, businesses, and even small industries across the country.
With falling solar panel prices, government support, and growing awareness about clean energy, off-grid solar systems in India are no longer a luxury—they are fast becoming a necessity. This in-depth guide explores how off-grid solar systems work, their cost, advantages, installation process, real-world use cases, and why they may define India’s energy future.
Table of Contents:
What Are Off-Grid Solar Systems?
Off-grid solar systems are standalone solar power setups that operate independently of the government electricity grid. Unlike grid-tied systems, they generate, store, and supply electricity without relying on external power sources.
These systems typically include:
- Solar panels
- Charge controller
- Battery storage
- Inverter
- Wiring and mounting structure
The defining feature of off-grid solar systems in India is energy storage. Electricity generated during the day is stored in batteries and used at night or during cloudy conditions, making them ideal for areas with unreliable or no grid access.
Why Off-Grid Solar Systems in India Are Gaining Popularity?
The demand for off-grid solar systems is rising rapidly due to a combination of economic, environmental, and practical reasons.
Key Growth Drivers –
- Frequent power outages
- Rising electricity tariffs
- Expansion of rural electrification
- Declining solar equipment costs
- Increased climate awareness
- Government push for renewable energy
India’s vast sunlight availability—averaging 300 sunny days per year—makes off-grid solar a natural fit for the country’s energy needs.
How Off-Grid Solar Systems Work (Step-by-Step)
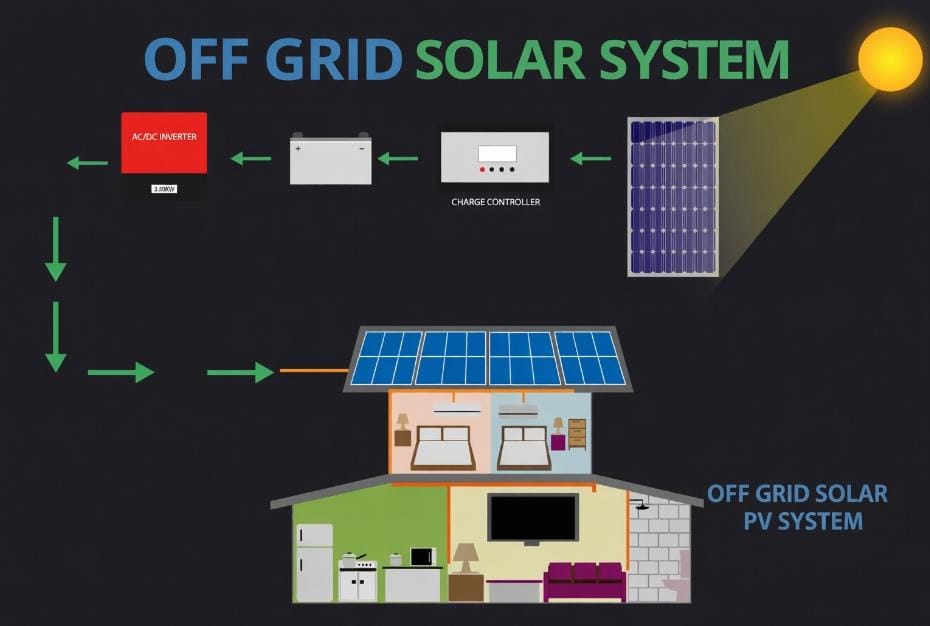
Understanding the working mechanism of off-grid solar systems in India helps users make informed decisions.
- Solar panels absorb sunlight and generate DC electricity
- Charge controller regulates voltage to protect batteries
- Batteries store energy for later use
- Inverter converts DC power into AC electricity
- Load supply powers appliances independently of the grid
This closed-loop system ensures uninterrupted power, even during grid failures.
Components of Off-Grid Solar Systems in India:
| Component | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Solar Panels | Convert sunlight into electricity |
| Charge Controller | Prevent battery overcharging |
| Batteries | Store excess energy |
| Inverter | Convert DC to AC |
| Mounting Structure | Secure panel placement |
Each component plays a critical role in the reliability of off-grid solar systems in India.
Cost of Off-Grid Solar Systems in India (2026 Estimate):
The cost of off-grid solar systems in India depends on capacity, battery type, and usage requirements.
| System Size | Suitable For | Approx Cost (₹) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 kW | Small homes | ₹90,000 – ₹1.3 lakh |
| 3 kW | Medium homes | ₹2.5 – ₹3.8 lakh |
| 5 kW | Large homes/farms | ₹4.5 – ₹6.5 lakh |
| 10 kW | Commercial use | ₹9 – ₹12 lakh |
Although initial costs appear high, long-term savings and zero electricity bills make off-grid solar systems in India financially viable.
Off-Grid vs On-Grid vs Hybrid Solar Systems:
| Feature | Off-Grid | On-Grid | Hybrid |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grid Dependency | None | Full | Partial |
| Battery Storage | Yes | No | Yes |
| Power During Blackouts | Yes | No | Yes |
| Installation Cost | High | Low | Medium |
| Ideal For | Remote areas | Cities | Mixed usage |
Among these, off-grid solar systems in India remain the best solution for energy independence.
On-Grid vs Off-Grid Solar System Comparison: Which Powers Your Needs Best?
Advantages & Disadvantages: A Balanced View
Advantages of Off-Grid Solar Systems in India:
- Absolute Energy Independence: Freedom from grid outages, load-shedding, and volatile electricity tariffs.
- Rural Electrification Champion: Brings transformative power to remote villages where grid extension is economically unviable.
- Zero Electricity Bills: After the payback period (typically 5-8 years), energy is virtually free for the battery’s lifespan.
- Environmentally Sustainable: Reduces carbon footprint and dependence on diesel generators, cutting noise and air pollution.
- Scalability: Systems can be designed to allow for future expansion as energy needs grow.
Disadvantages & Challenges:
- High Initial Investment: The need for a large battery bank significantly increases upfront cost compared to on-grid systems.
- Battery Replacement & Maintenance: Batteries have a finite lifespan and represent a recurring replacement cost. They also require proper ventilation and maintenance.
- Energy Management Required: Users must be mindful of consumption, especially during consecutive cloudy days, to avoid draining the battery bank excessively.
- Space Requirements: Adequate space is needed for both solar panels and the battery bank, which can be substantial for larger systems.
Limitations You Should Know:
While powerful, off-grid solar systems in India have some challenges:
- Higher upfront cost due to batteries
- Battery replacement every 5–8 years
- Requires accurate load planning
- Needs professional installation
However, technological advancements are rapidly reducing these limitations.
Who Should Choose Off-Grid Solar Systems in India?
The applications for off-grid solar power systems across India are vast and impactful:
- Residential: Powering homes in off-grid villages, farmhouses, and hilly terrains (e.g., Ladakh, Northeast states).
- Agricultural: Running water pumps for irrigation, powering cold storage units for produce, and operating dairy equipment.
- Commercial: Supporting small shops, rural ATMs, petrol pumps, and roadside eateries (dhabas).
- Institutional: Ensuring uninterrupted power in rural schools, healthcare centres (PHCs) for vaccine refrigeration, and community centres.
- Telecom: Powering remote mobile towers, a critical application for connectivity.
- Tourism: Eco-resorts, campsites, and wildlife lodges in sensitive areas use off-grid solar for sustainable operations.
For these users, off-grid solar systems in India provide reliability where the grid fails.
Government Support & Subsidy Landscape
While subsidies focus more on grid-connected systems, some state-level programs and rural development missions support off-grid solar systems in India, especially for:
- Agriculture
- Tribal areas
- Border villages
- Public infrastructure
Low-interest loans and NABARD-backed financing options also improve affordability.
Installation Process Explained:
Installing off-grid solar systems in India involves:
- Load assessment
- Site inspection
- System design
- Equipment procurement
- Installation and wiring
- Battery configuration
- Testing and commissioning
Professional installation ensures efficiency, safety, and long system life.
Maintenance Tips for Long-Term Performance
- Clean panels every 2–3 weeks
- Monitor battery health
- Avoid deep battery discharge
- Keep inverter ventilated
- Annual system inspection
Proper care extends the life of off-grid solar systems in India beyond 25 years for panels.
Market Growth & Future Outlook:
The off-grid solar market in India is expected to grow at double-digit rates through 2030. With improvements in lithium battery technology and falling storage costs, off-grid solar systems in India are likely to become mainstream even in urban homes.
Industry experts predict a major shift from diesel generators to off-grid solar, especially in commercial and agricultural sectors.
Off-Grid Solar Systems vs Diesel Generators:
| Factor | Off-Grid Solar | Diesel Generator |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel Cost | Zero | High |
| Noise | Silent | Loud |
| Pollution | None | High |
| Maintenance | Low | High |
| Long-Term Cost | Low | Very High |
This comparison explains why off-grid solar systems in India are replacing generators rapidly.
Real-Life Impact: Changing Lives on the Ground
From lighting homes in tribal belts to powering cold storage units for farmers, off-grid solar systems in India are improving education, healthcare, livelihoods, and safety. Students can study at night, clinics can store vaccines, and farmers can irrigate crops reliably.
FAQs: Off-Grid Solar Systems in India
Q1: Can an off-grid solar system run an air conditioner (AC)?
A: Yes, but it requires careful design. A 1.5-ton AC (~1500W) requires a significantly larger system (typically 5kW+ solar and a substantial lithium battery bank) to run for extended periods, especially at night.
Q2: What happens during long periods of rain or monsoon?
A: A well-designed system includes “days of autonomy” in the battery bank. For critical needs, a backup generator (diesel/solar-biogas) can be integrated to recharge batteries when solar input is low for many days.
Q3: Are there government subsidies for off-grid solar systems in India?
A: Yes. While major central subsidies focus on grid-connected rooftop systems, schemes like PM-Surya Ghar and various state renewable energy programs offer financial incentives for off-grid and decentralized solar projects, especially for rural and agricultural use.
Q4: How long do the batteries last, and what is the maintenance?
A: Lead-acid batteries last 3-5 years and require regular topping up with distilled water and terminal cleaning. Lithium-ion batteries last 8-12+ years with virtually no maintenance but cost 2-3 times more upfront.
Q5: Is off-grid solar a good business opportunity in India?
A: Absolutely. The market for off-grid solar systems in remote and underserved areas is enormous. Entrepreneurship opportunities range from being a system installer and service provider to starting a solar franchise for products like solar water pumps and home lighting systems.
Final Verdict: Why Off-Grid Solar Systems in India Matter
The journey toward a solar-powered India is paved with both grid-connected and off-grid solutions. For a significant portion of the country, off-grid solar systems represent more than just technology; they symbolize empowerment, resilience, and inclusive development. As battery costs continue to decline and technology improves, the economic case for going off-grid will only strengthen.
Investing in an off-grid solar system in 2025 is an investment in unshakeable energy security. It promises liberation from power cuts, a stable cost of electricity, and a direct contribution to a cleaner nation. For homeowners and business owners in areas where the grid is a distant promise or a persistent letdown, embracing an off-grid solar system is the most practical step toward a self-reliant and sustainable future.
With rising power demand and climate challenges, off-grid solar systems in India are not just an alternative solution; they are a cornerstone of India’s clean energy revolution.






